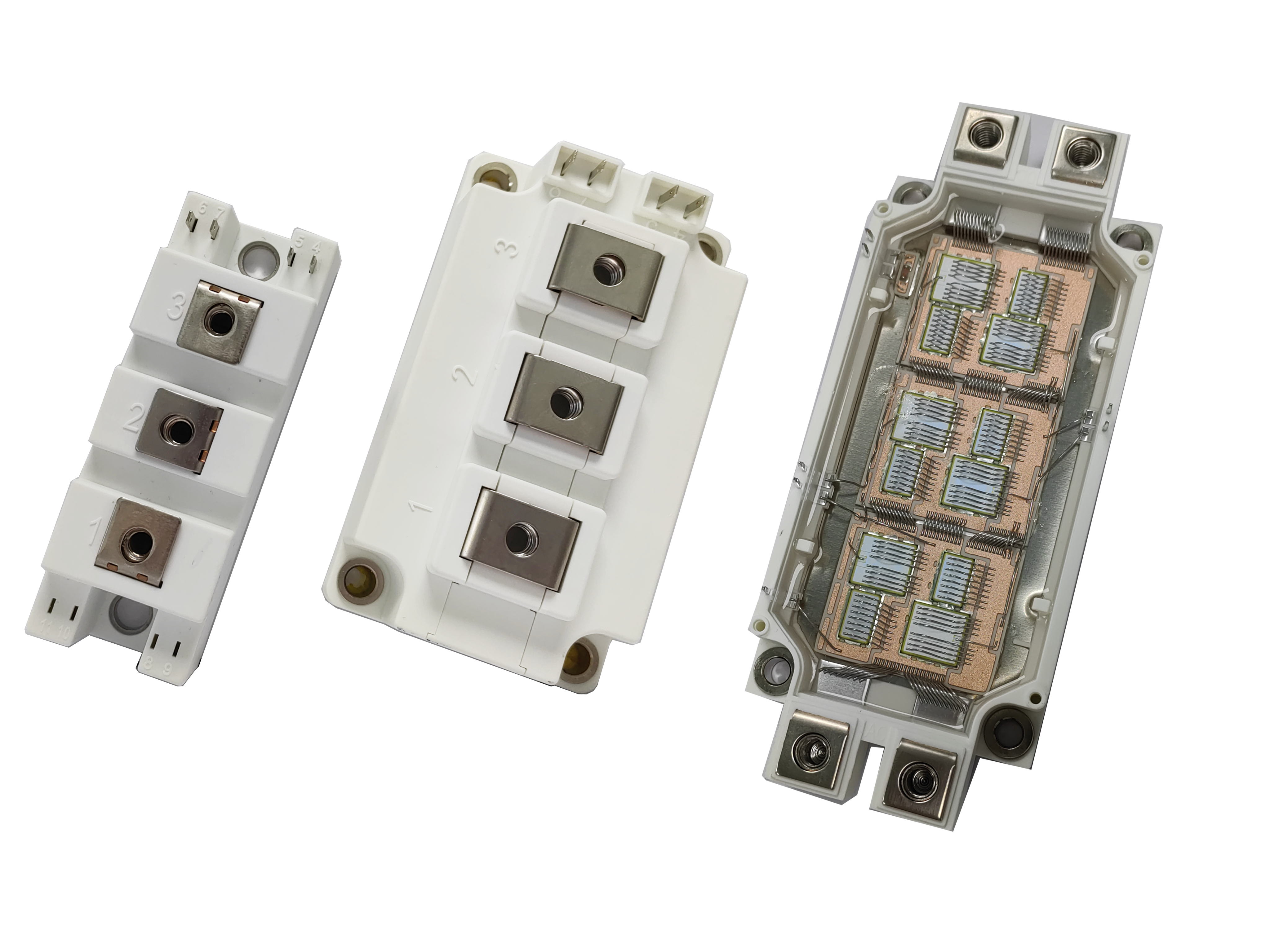
Detailed Technical Specifications and Applications of Industrial Thyristor Modules
Thyristor modules are pivotal components in modern power electronics, engineered to deliver reliable switching and control in high-voltage and high-current environments. These modules are essential in numerous sectors—from welding systems and desalination plants to precision diming operations—due to their efficient phase control and surge resilience. This article outlines the critical specifications and operational benefits of dual thyristor modules in detail.
Core Electrical Specifications
At the heart of the thyristor module is its switching capability, designed for both unidirectional and bidirectional current conduction. A hallmark characteristic of dual thyristor modules is their capacity for industrial phase control, which allows fine modulation of power delivery across resistive and inductive loads.
Some of the core specifications include:
High surge current capacity: Enables the module to handle peak currents without degradation, ideal for dynamic loads like welding equipment or variable motor drives.
Low on‑state voltage: Minimizes power loss and heat generation, leading to improved system efficiency and component longevity.
High repetitive peak off-state voltage (up to 1600V) makes these modules suitable for medium- to high-voltage industrial applications.
Construction and Material Engineering
Dual thyristor modules are designed using advanced silicon die technology, integrated into compact housing with metal-ceramic substrates. These materials provide thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, making them suitable for harsh operational environments.
The use of isolated baseplates enables safe mounting and simplifies the heat sinking process. In environments like desalination facilities or food packaging lines where humidity and vibration are constant, such construction ensures durability and consistent performance.
Sector-Specific Applications
These modules find their utility in a diverse range of industries:
Welding: Modules enable precise control of current pulses, resulting in smoother arc ignition and reduced electrode wear.
Desalination: The ability to sustain power in high-moisture, high-temperature environments is critical for pump drives and thermal distillation control systems.
Diming systems: Utilized in lighting applications, the modules enable flicker-free brightness modulation, reducing eye strain and energy consumption.
Additionally, data centers rely on these thyristor modules for redundancy and UPS switching. With their low on‑state voltage, they reduce energy overhead—crucial in 24/7 operational facilities.
Interface and Control
The modules typically feature dual anti-parallel thyristors with isolated gate connections. This architecture allows them to integrate seamlessly with modern gate drivers, PLCs, and digital controllers.
Industrial phase control is achieved by triggering the thyristors at variable points in the AC waveform, effectively controlling power flow without mechanical components. This not only improves precision but also reduces noise and maintenance.
Safety and Reliability Features
Beyond performance, modern dual thyristor modules incorporate:
Integrated snubber circuits for voltage spike suppression.
Short-circuit ruggedness.
Insulated and sealed enclosures for EV charger environments and laser systems where electrical noise isolation is critical.
Electromagnetic shielding for sensitive radar systems.
Their high surge current handling makes them reliable in mission-critical applications where failure is not an option.