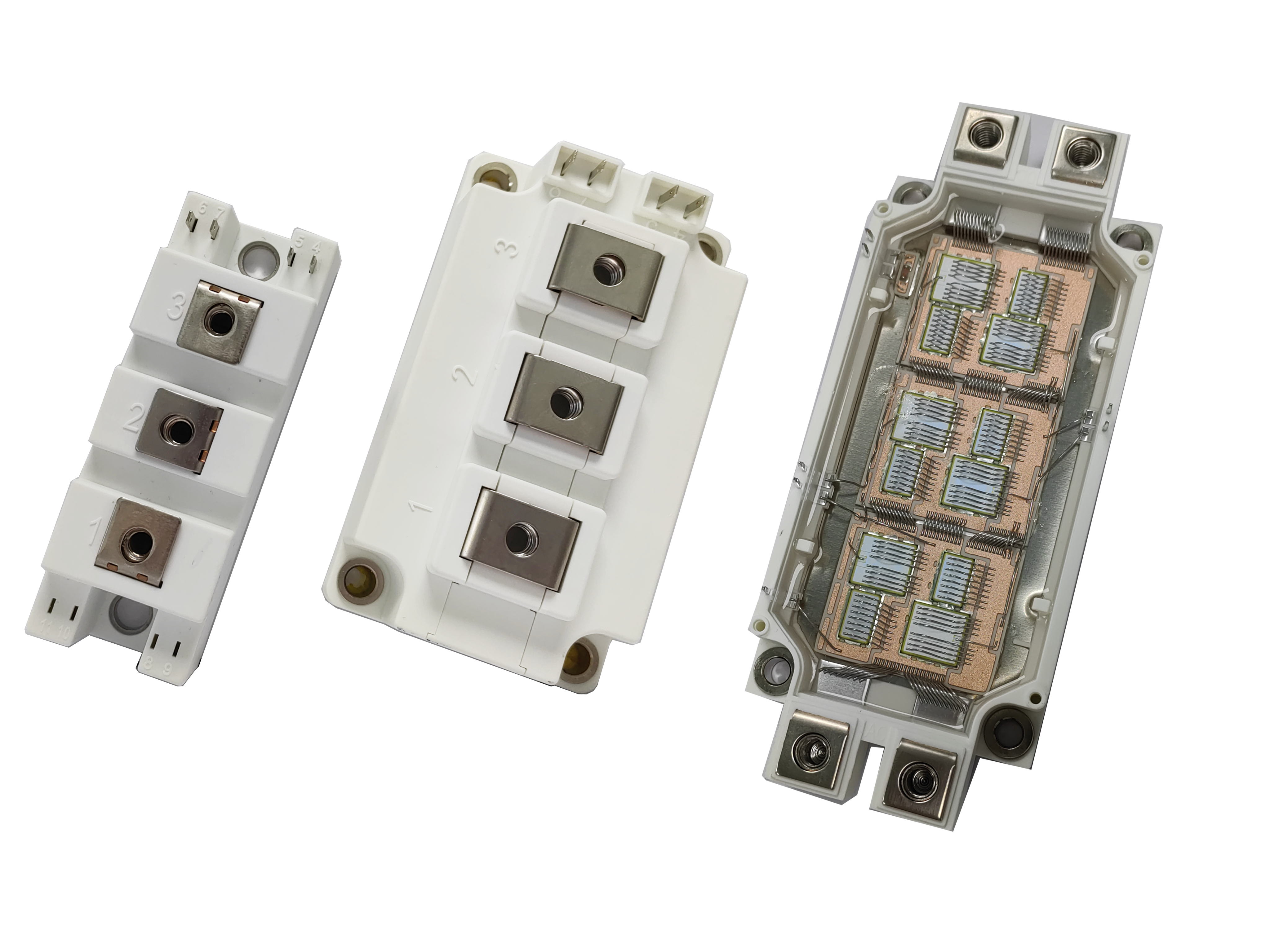
Replacing Industrial Thyristor Modules: Key Procedures for Electrolysis Rectifiers
In high-power applications like electrolysis rectifiers, the precision and performance of thyristor modules are critical to system efficiency. Over time, even the most rugged components can wear out, necessitating a structured replacement process. This article outlines essential steps for replacing high-performance dual thyristor modules, ensuring continued reliability under heavy-duty conditions.
Why Thyristor Module Replacement Is Necessary
Electrolysis rectifiers operate continuously under high load and fluctuating temperatures. Signs that the ultra low VT desalination smart grid High surge current low on‑state voltage industrial phase control dual thyristor module may need replacing include unstable current flow, abnormal heat dissipation, or inconsistent triggering.
These ultra low VT desalination smart grid High surge current low on‑state voltage industrial phase control dual thyristor module units are engineered for critical applications like desalination and grid power control, but long-term exposure to high surge currents can degrade performance. Routine inspections and scheduled replacement help prevent full system shutdowns.
Preparing the System and Ensuring Safety
Before beginning replacement, shut down the entire power unit and confirm that capacitors and other components have fully discharged. In battery charging systems with tight regulation, like those using soft-start battery charger temperature control High surge current low on‑state voltage industrial phase control dual thyristor module, ensuring complete disconnection is vital to technician safety.
Operators should use thermal gloves, grounding straps, and insulated tools. Pre-replacement photos of the wiring layout can be helpful during reassembly. Carefully document control leads, triggering circuitry, and heat sink interface materials.
Proper Removal and Cleaning Process
Removing a worn thyristor module requires patience. Disconnect power and signal terminals and unscrew the module from its mounting surface. If using a soft-start battery charger temperature control High surge current low on‑state voltage industrial phase control dual thyristor module, take care to retain the correct thermal pad placement and note any heat damage.
Thoroughly clean the module base, removing old thermal paste and inspecting for signs of heat-induced warping or corrosion. The new module should only be installed on a clean, flat, and dry surface to ensure proper thermal transfer.
Installation and Calibration of New Module
Insert the replacement HVDC power factor diming High surge current low on‑state voltage industrial phase control dual thyristor module into position, ensuring mounting holes align correctly. Apply a fresh layer of thermal paste and secure the module using a torque wrench per manufacturer guidelines.
Reconnect all wiring carefully, referencing earlier documentation. Ensure the gate trigger circuit is functioning properly and calibrate phase control timing. In HVDC and power factor diming systems, accurate phase control is essential to prevent waveform distortion and electrical inefficiency.
During the first startup, activate the rectifier using soft-start mode to slowly introduce current and allow the module to reach thermal equilibrium. Monitor system temperature and current behavior over the next several operating cycles.
Post-Replacement Validation and Routine Checks
After installation, check the output waveform using an oscilloscope and verify gate pulse performance. The ultra low VT desalination smart grid High surge current low on‑state voltage industrial phase control dual thyristor module, along with the HVDC power factor diming High surge current low on‑state voltage industrial phase control dual thyristor module, both benefit from scheduled IR testing and thermal imaging diagnostics.
Create a logbook entry for each replacement procedure, noting the module model, batch number, and installation details. For rectifiers in mission-critical operations like desalination plants or industrial battery rooms, proactive monitoring extends module lifespan and avoids expensive unplanned outages.