Understanding the Phase Control Thyristor (Stud): Design, Applications, and Key Features
The Phase Control Thyristor (Stud), often referred to as a "Stud SCR," is an essential component in modern power electronics, particularly in AC control and power conversion applications. The stud configuration offers improved thermal management, robust current handling, and high reliability. This article will explore the working principles, key features, and applications of the Phase Control Thyristor (Stud), offering insights into why it is a preferred choice for high-power industrial systems.
What is a Phase Control Thyristor (Stud)?
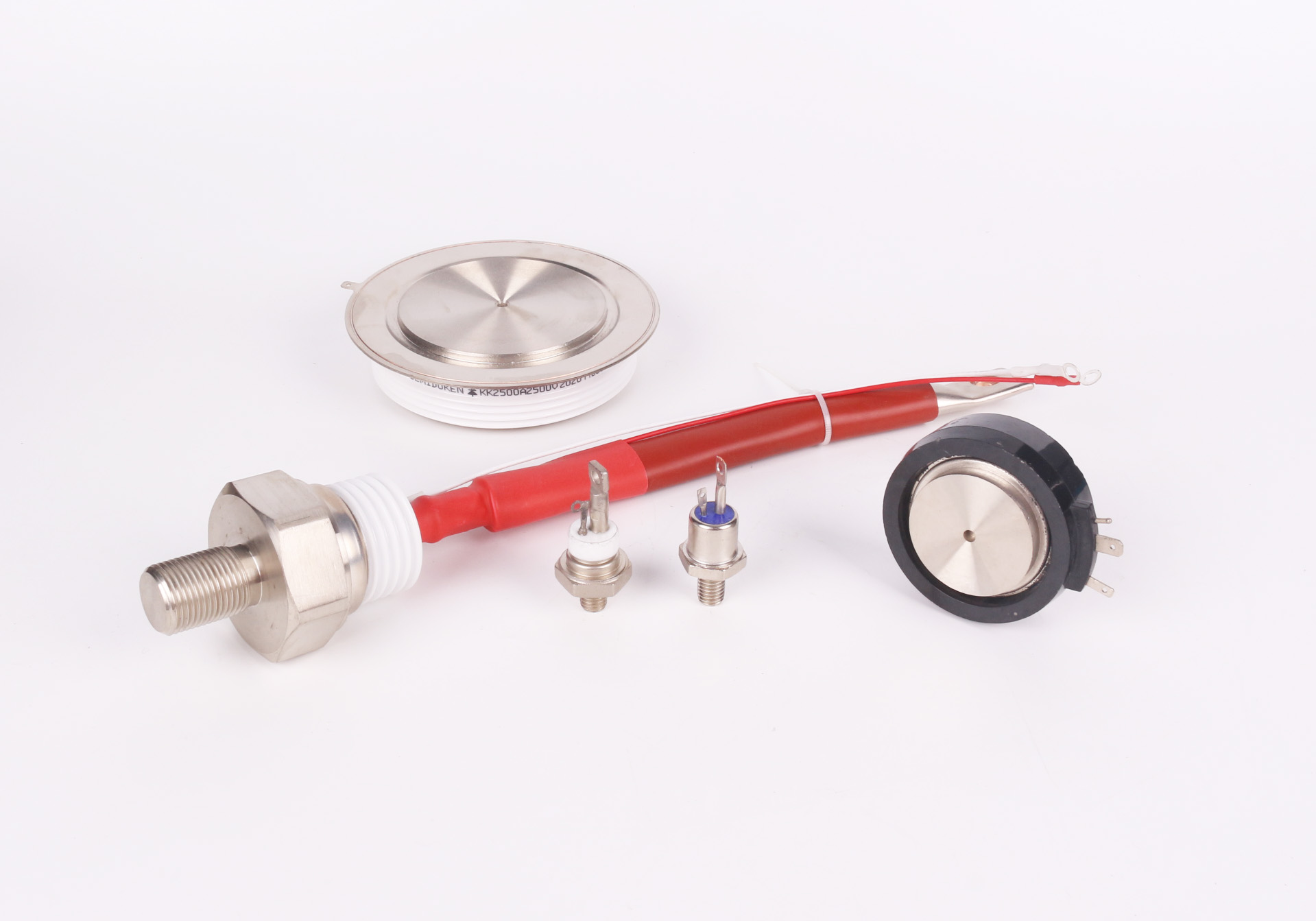
A Phase Control Thyristor (Stud) is a type of silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) designed for controlling large amounts of electrical power in AC circuits. It features a "stud" design, where the device’s anode is connected to a stud, allowing for better heat dissipation and easier integration into power control systems. The stud configuration is ideal for applications that require high current and voltage handling, and it enhances the overall mechanical and thermal characteristics of the thyristor.
Phase control thyristors operate by being turned on via a gate signal, allowing current to flow from the anode to the cathode. Once turned on, the thyristor remains conducting until the current falls below a certain threshold or the voltage is reversed. This ability to control the power flow makes phase control thyristors ideal for applications that demand precise control of AC power.
Key Features of the Phase Control Thyristor (Stud)
1. High Current Handling
One of the most significant advantages of the stud design is its ability to handle high currents. Phase control thyristors in the stud package can manage several hundred to thousands of amperes of current, making them ideal for high-power applications such as industrial drives, electric arc furnaces, and power supplies.
2. Robust Voltage Ratings
Phase control thyristors in stud configurations can also support high voltage ratings, often ranging from hundreds to thousands of volts. This enables them to be used in various demanding applications where high voltage is present, including power conversion systems and high-voltage rectifiers.
3. Efficient Thermal Management
The stud configuration helps improve heat dissipation. As the stud is often bolted onto a heatsink, it provides an efficient path for thermal energy to escape. This helps prevent overheating, which can reduce the lifespan and performance of the thyristor. Proper thermal management is crucial in high-power systems where heat buildup could otherwise damage the device.
4. Durability and Reliability
Due to their rugged design and high thermal capacity, Phase Control Thyristors (Stud) are highly reliable and durable in harsh industrial environments. They are resistant to mechanical stress and have excellent surge withstand capabilities, ensuring long-term, trouble-free operation in critical power control systems.
Applications of Phase Control Thyristors (Stud)
1. Motor Control and Drives
In motor control systems, Phase Control Thyristors (Stud) regulate the amount of AC power supplied to electric motors, enabling smooth speed control. By adjusting the phase angle of the thyristor, engineers can control the voltage delivered to the motor, providing fine-tuned control of motor speed and torque. This makes the stud thyristor a key component in variable speed drives (VSDs) used in conveyors, pumps, and fans.
2. Industrial Heating
Phase Control Thyristors (Stud) are used in industrial heating applications, such as furnaces and ovens, to regulate the power supplied to heating elements. The ability to precisely control the power allows for accurate temperature regulation and energy savings, making the stud thyristor the preferred choice in electric heating systems.
3. Power Conversion Systems
In power conversion systems, Phase Control Thyristors (Stud) are used for rectification, where AC power is converted to DC. This is essential in HVDC transmission, renewable energy systems (like wind and solar), and electric vehicle chargers. The thyristor’s ability to control the flow of power ensures stable and efficient operation in these systems.
4. Surge Protection
Due to their fast switching capabilities, Phase Control Thyristors (Stud) are also used in surge protection systems. When a surge is detected, the thyristor can quickly switch on and divert excess current away from sensitive components, preventing damage and enhancing the system's reliability.
Advantages of Using Phase Control Thyristors (Stud)
1. Precise Control
Phase Control Thyristors (Stud) offer precise control over AC power, which is essential for applications requiring variable voltage, current, and frequency. This makes them highly suitable for industrial automation, robotics, and various manufacturing processes.
2. Long Lifespan
Due to their durable design and efficient thermal management, stud thyristors typically have a long operational life, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement in heavy-duty applications.
3. Flexibility and Adaptability
The versatility of Phase Control Thyristors (Stud) allows them to be used in a wide range of applications, from small devices to large-scale industrial systems. This flexibility makes them a go-to solution for power engineers across multiple industries.
Conclusion
The Phase Control Thyristor (Stud) is an essential component for high-power industrial applications that require reliable, efficient, and precise control of AC power. Its robust construction, efficient thermal management, and ability to handle high current and voltage ratings make it an ideal solution for motor control, industrial heating, power conversion, and surge protection systems. For engineers looking to improve the efficiency and reliability of their power control systems, the Phase Control Thyristor (Stud) offers an indispensable solution.