Evaluating Forward Conduction Performance in 200A 400V Diodes for Power Applications
Forward conduction loss is generated whenever current flows through a diode in the forward-biased condition. It manifests as a voltage drop across the junction, and the resulting heat can negatively affect both the diode and surrounding circuitry if not properly managed. In high-current environments, such as those employing a 200A 400V fast recovery diode, managing this loss is essential to avoid performance degradation.
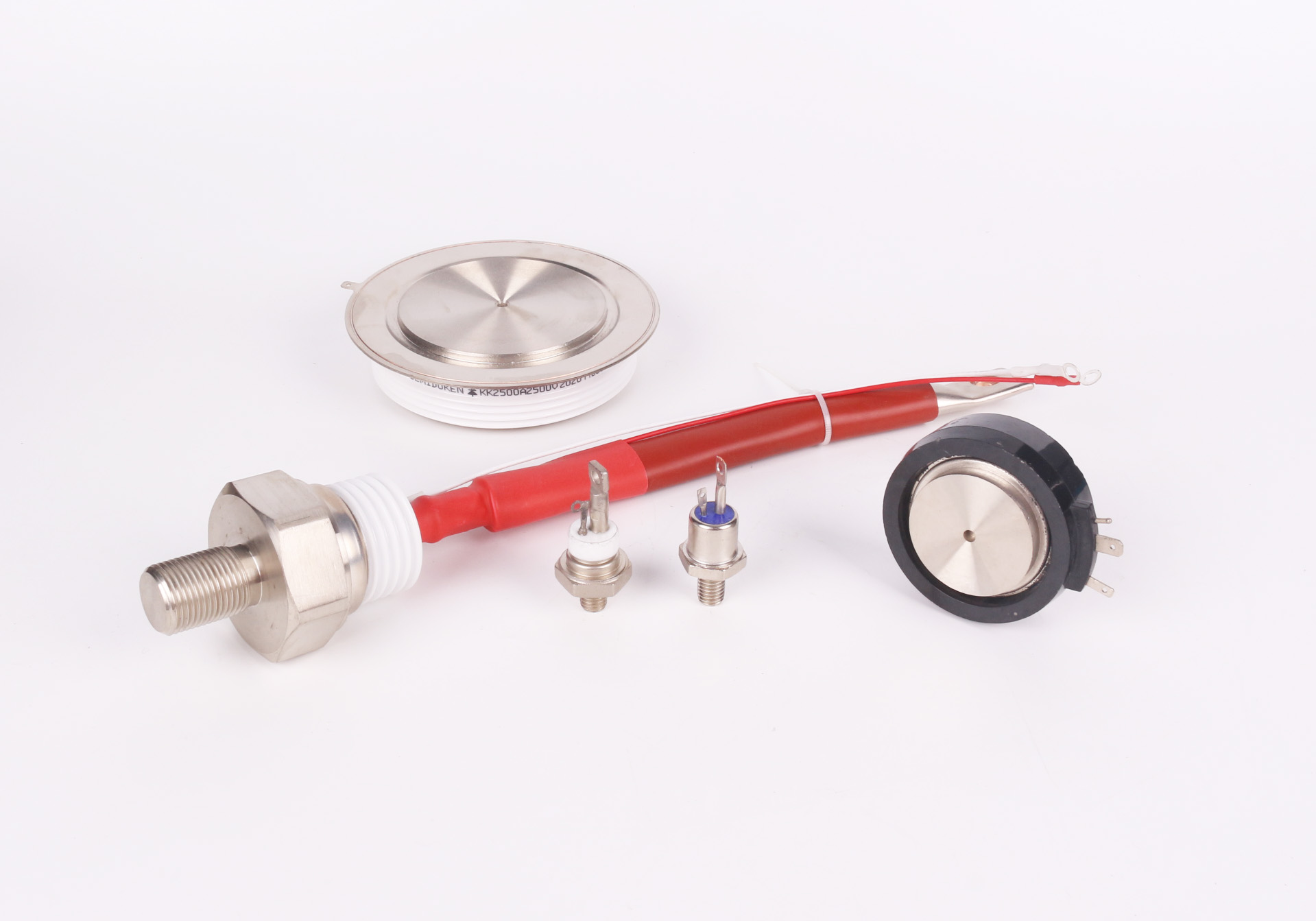
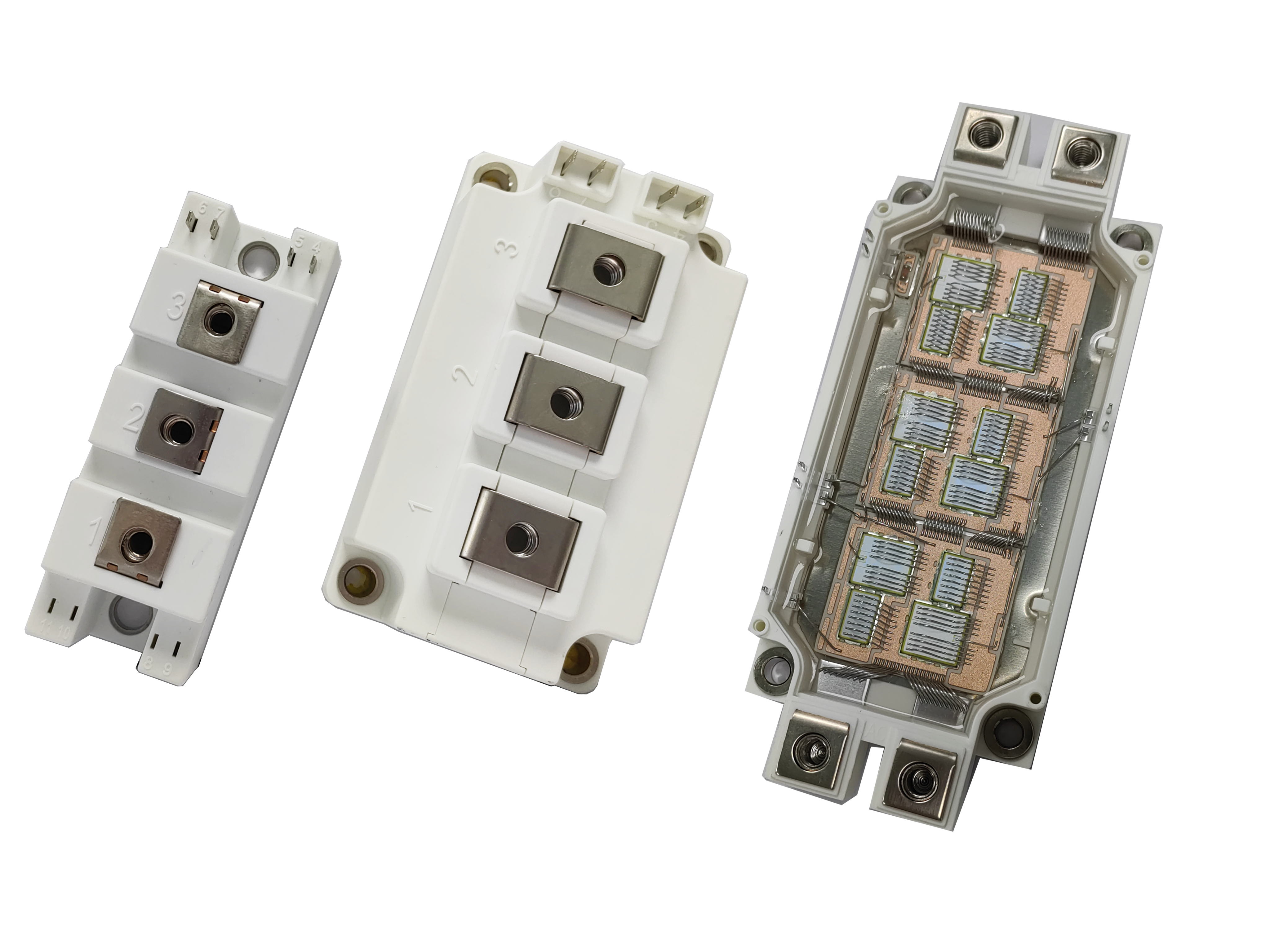
Diodes using a 3/4″-16UNF stud type mechanical mounting are specifically designed to offer excellent thermal dissipation and mechanical stability in automotive applications. These designs promote solid connections and reduce the risk of component failure under vibration or heat cycling, making them ideal for EV power modules and DC/DC converters that require high reliability.
Specialized Configurations for Industrial Use
Industrial systems that rely on dual diode for inverter drives require fast recovery, high thermal capacity, and minimal conduction losses to ensure continuous operation under variable load conditions. In such configurations, maintaining a low conduction loss is essential for minimizing thermal stress and extending system life.
In welding environments, high-frequency switching and continuous current demands push components to their limits. The common anode low conduction loss used in welding machine 200A 400V fast recovery diode performs well by minimizing energy loss during each conduction cycle, leading to reduced heat buildup and longer operational periods between maintenance cycles.
The Mechanical Design Advantage
The 3/4″-16UNF stud type diode packaging is a preferred choice in demanding environments. It offers secure mounting and excellent thermal transfer to the heat sink. In both automotive applications and heavy-duty inverter systems, this stud type configuration ensures firm electrical contact while reducing inductance and enhancing performance under pulsed loads.
The common anode configuration, often used in welding machines, reduces circuit complexity and lowers conduction resistance, making it easier to implement efficient current paths. When paired with 200A 400V fast recovery diodes, it ensures consistent current delivery even in harsh conditions, delivering both low conduction loss and high reliability.
Forward Conduction Testing and Optimization
To measure forward conduction loss in practical setups, engineers simulate real-world load conditions and monitor heat output, voltage drops, and switching efficiency. For dual diode for inverter drives, the evaluation includes checking thermal balance between the two junctions and monitoring peak reverse recovery time to maintain system synchronization.
Advanced testing may also include thermal cycling, high-current pulse testing, and vibration endurance—all of which confirm whether the diode design meets rigorous automotive application standards.
Balancing Loss and Longevity
A key goal in modern diode design is to reduce forward conduction loss without compromising switching performance or thermal endurance. Manufacturers now use materials and construction methods that enhance junction uniformity and reduce resistance. In turn, this allows 200A 400V fast recovery diodes to meet both energy efficiency and high reliability goals across use cases ranging from inverter drives to welding machines.